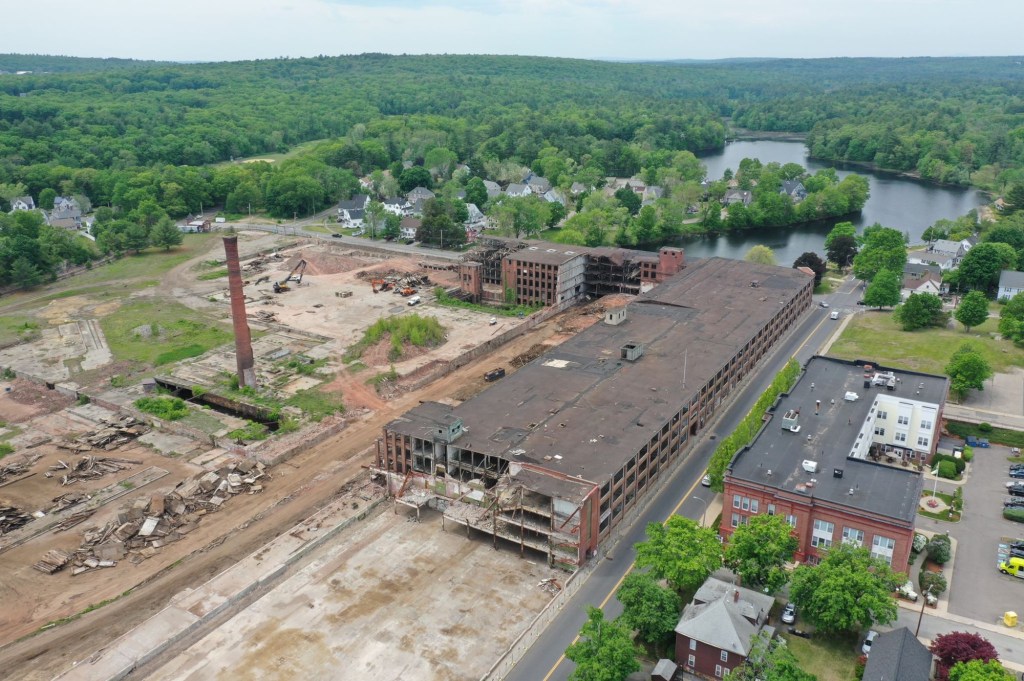
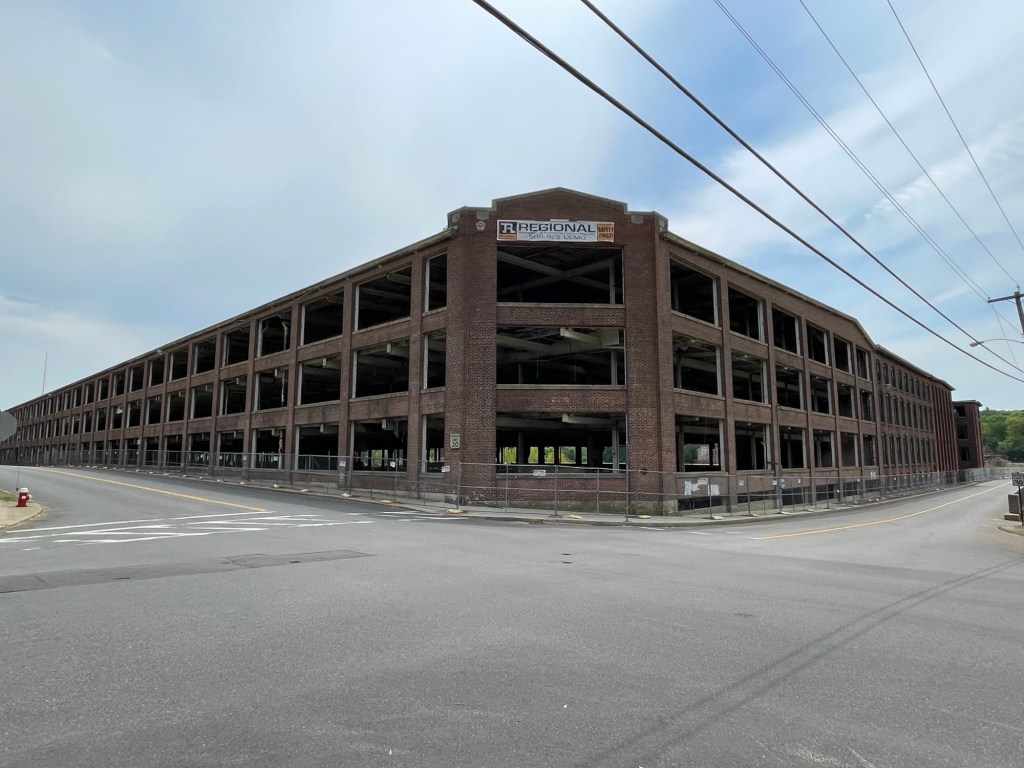
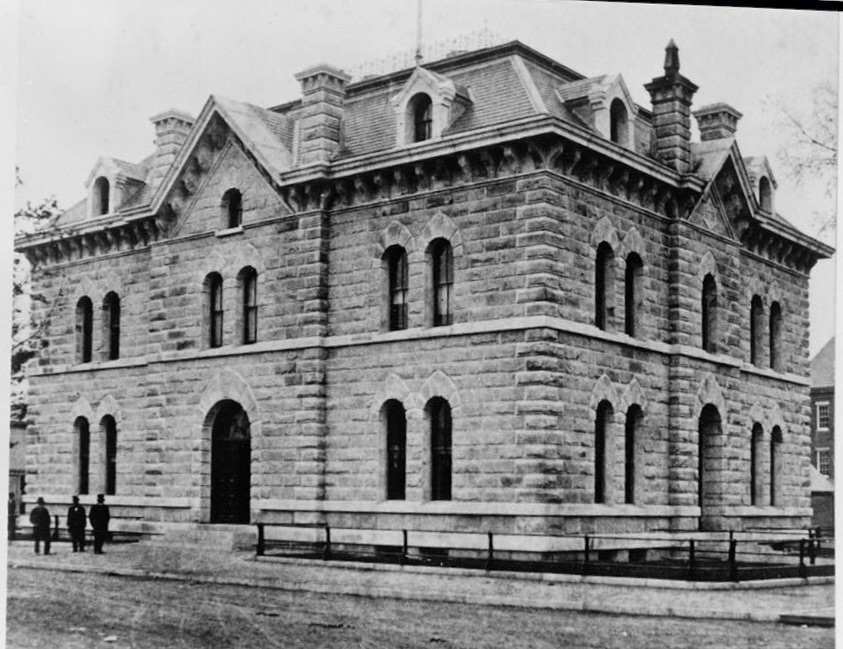
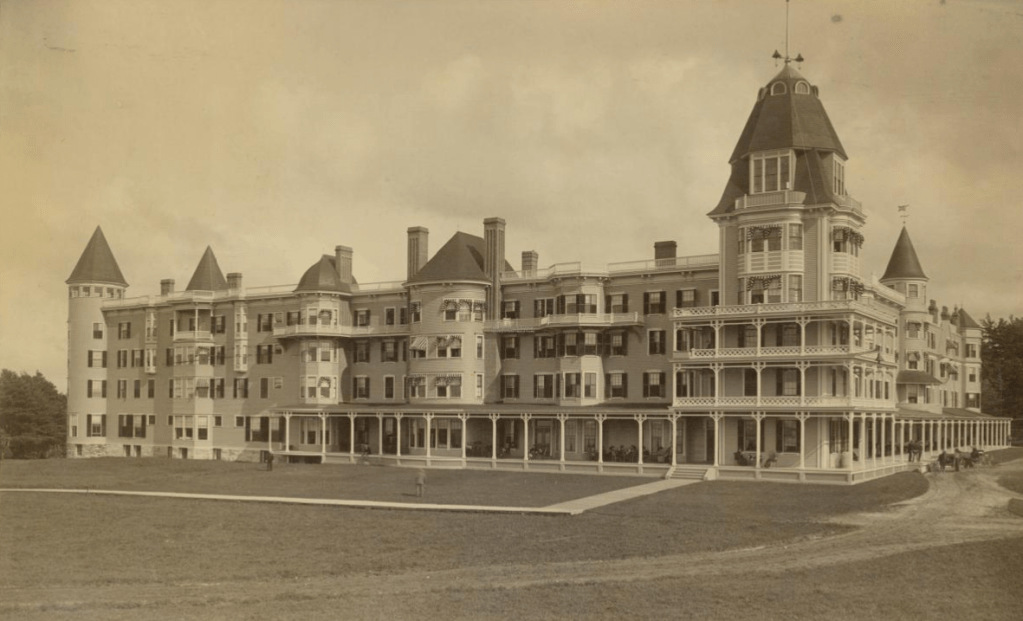
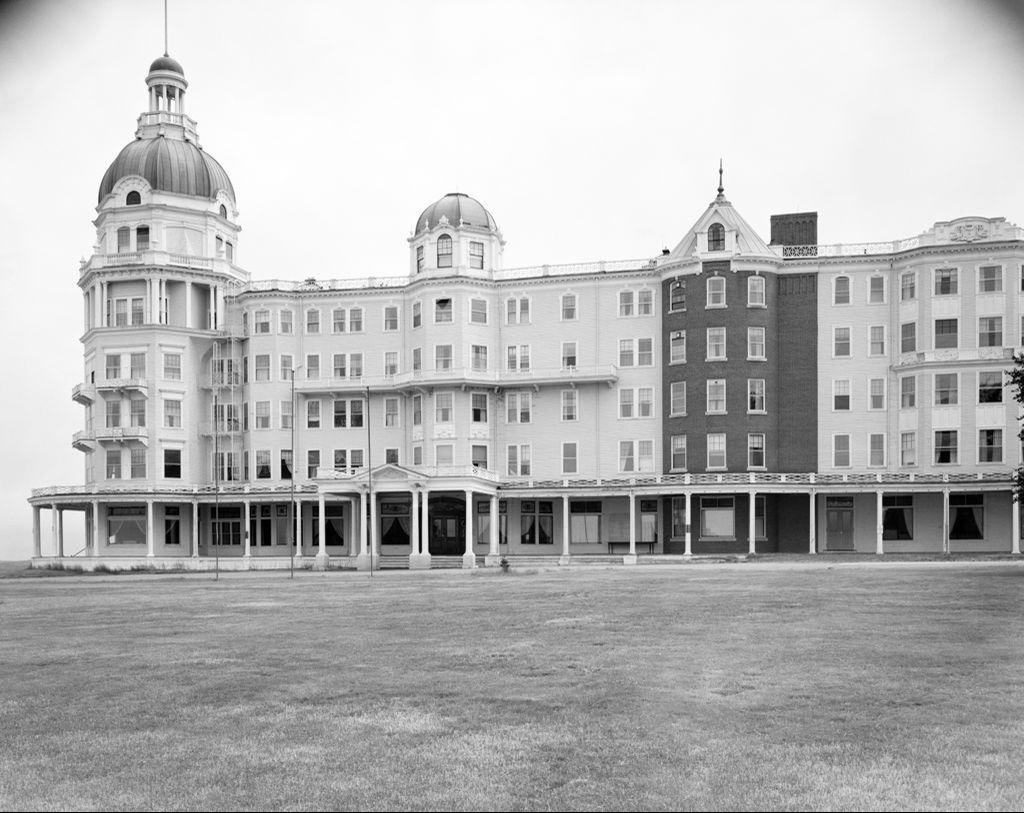
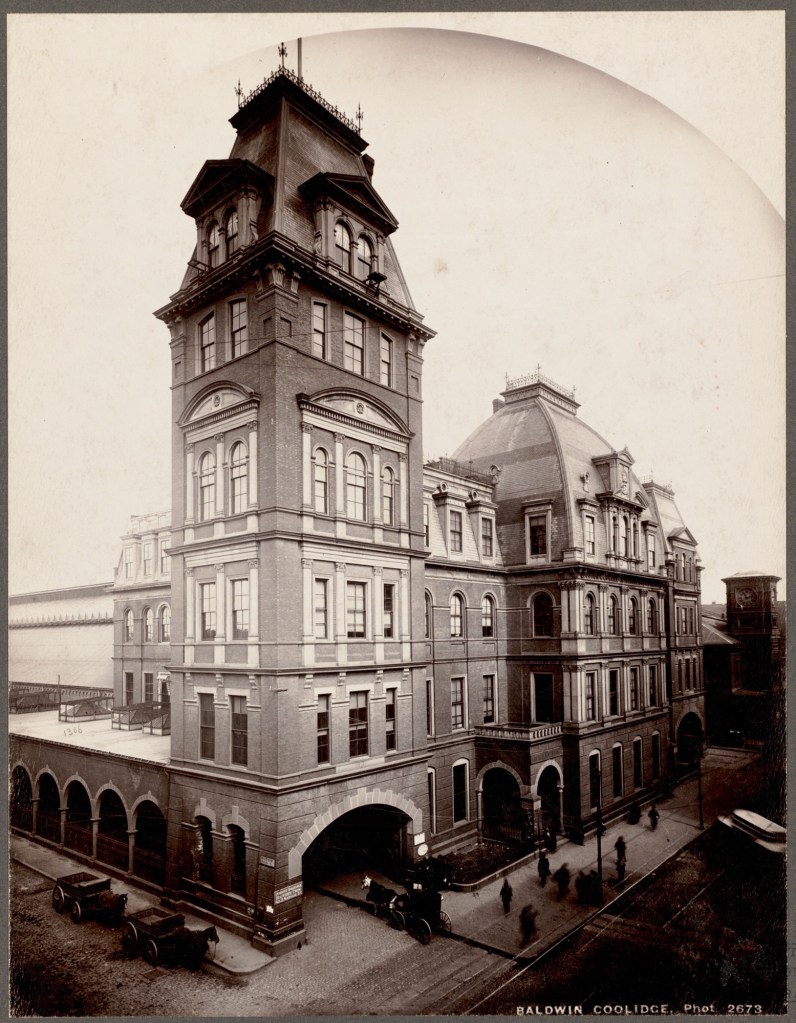
Hopedale, Massachusetts separated from Milford and incorporated in 1886. The “downtown” of the community encompasses industrial, institutional, and residential buildings in Hopedale Village, also known as Draper Village after the long-driver of the local economy, Draper Corporation. Hopedale was largely developed as a planned company town, and its architectural significance and ultimate preservation was largely due to the success of the Draper Corporation as majority owner until the 1950s. The Draper Corporation was originally a small operation in Hopedale in 1841 managed by George Draper (1817-1887), but grew exponentially thanks to his son, George Albert Draper (1855-1926), who had a passion for finding innovative technology to make the production of cloth more efficient. He led the company’s charge to become the nation’s leading producer of machines for the cloth-making industry. In the ensuing decades the factory village of Hopedale became a “model” company town under his leadership, with the business controlling every aspect of the town and worker life in a paternalistic program that extended beyond social structure to include architecture and urban planning of the village. The company developed hundreds of homes for workers, a town hall, library, churches, schools, a fire station, and recreational facilities, along with its factory complex at the center. In1892, with the advent of the Northrop Loom, Draper became the largest producer of textile machinery in the country. Due to their success at the end of the 19th century, much of the complex was built and rebuilt in fire-proof brick factory buildings with large windows to allow light and air into the facilities. Draper’s dominant position within the textile machine manufacturing industry began to erode shortly after World War II, and the company began to sell its company houses to their occupants as private homes in 1956. During the 1960s American textile machinery makers such as Draper lost their technological leadership to foreign manufacturers due to cheap labor, and the general American textile industry collapsed. The plant eventually closed in 1980, and sat vacant until it was decided by the local officials to raze the once great complex, as adaptive reuse was not feasible in the market for such large structures. The mill was demolished in the summer of 2021 and the lot at the center of town remains a brownfield site.