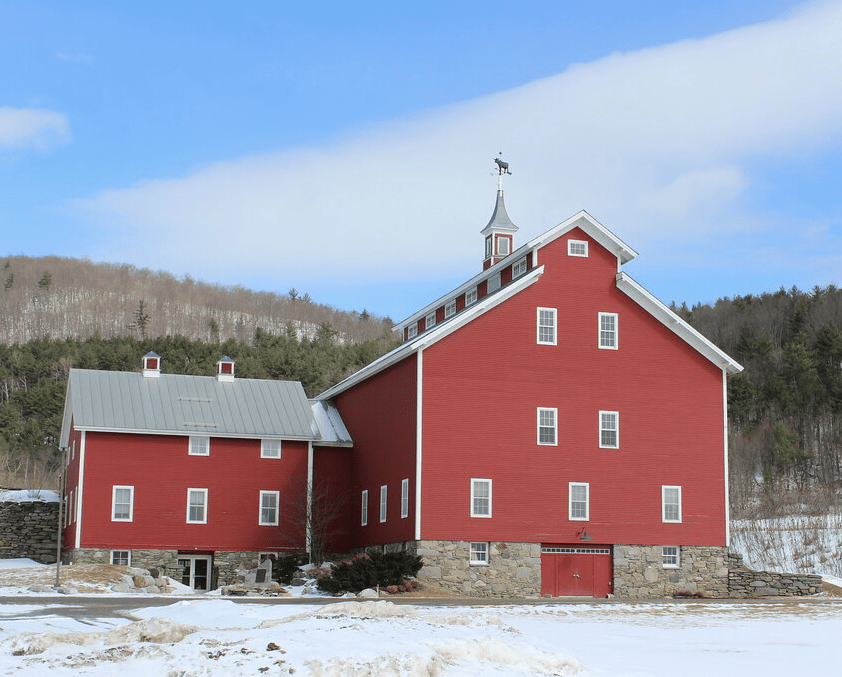
Located in Richmond, Vermont, this four-and-a-half-story, wood-frame barn with striking monitor roof, is one of two nearly identical such barns on adjacent farms in the small rural farming community. In 1871, Uzziel Stevens Whitcomb (1817-1899) and his brother, acquired adjacent farms on East Main Street in the Winooski River Valley. Uzziel’s farm grew and he created one of the largest dairy farms in Vermont, spanning around six hundred acres with about 120 cows. Uzziel’s son, Moses S. Whitcomb (1842-1933), continued his father’s massive dairy farm and acquired nearby farms, growing his property to span over 900-acres of farmland. In 1901, with one of the largest dairy farms in the state, he erected the first and larger barn, now known as the East Monitor Barn, and in 1904, added a second to the west, the West Monitor Barn. Unlike many barns west of the Green Mountains, this one followed the more traditional northern New England bank barn design with a manure basement, cow stables on the second floor, and two-floors of hay storage above. The barn is now commonly used as a venue for weddings and other special events!








