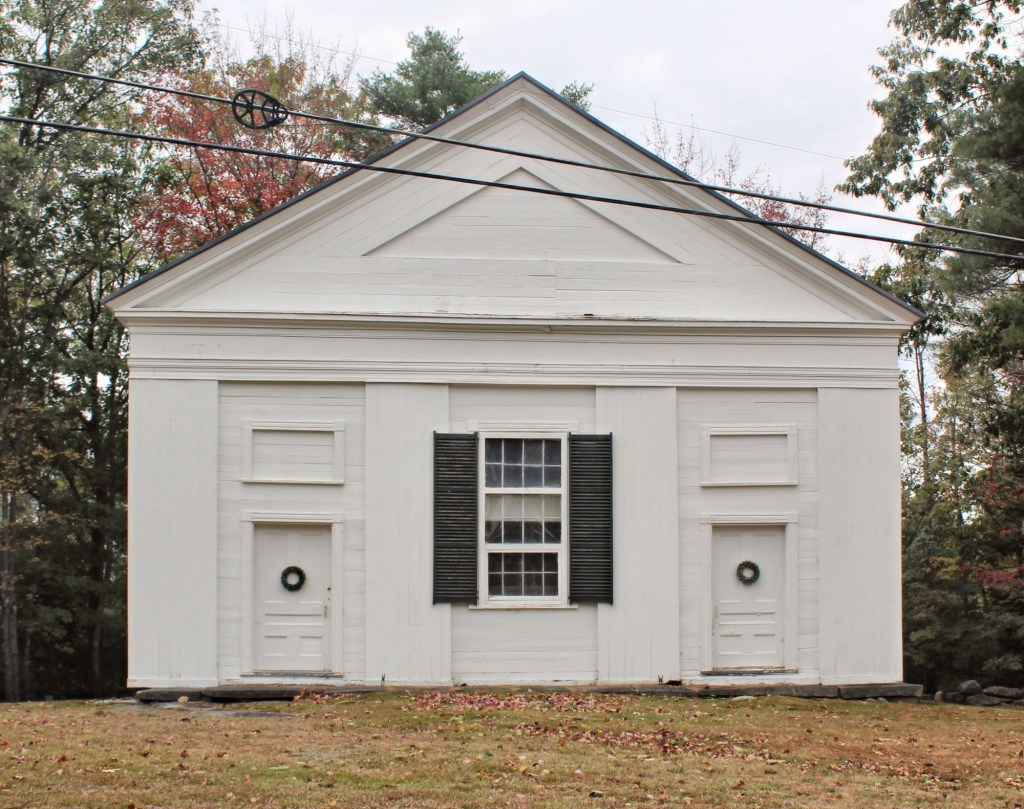
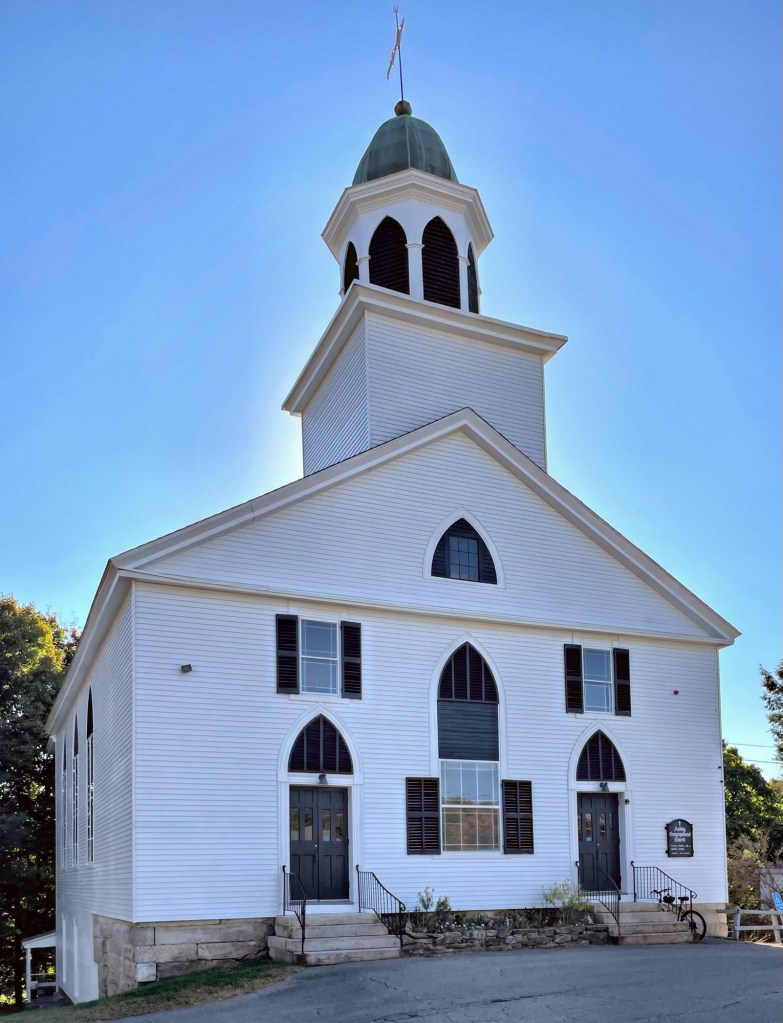
Constructed in 1839 by local carpenter/builder Jeremiah Cotton, the Universalist Meeting House of New Gloucester, Maine, is a dignified example of the Greek Revival style in a rural context. The First Universalist Society of Christians in New Gloucester was organized in 1805 with members drawn from nearby communities including those of Gray and Poland. In 1830, the congregation reorganized itself into the First Universalist Society of New Gloucester and Pownal. During its early history services were apparently held at various places in the community for it was not until November of 1838 that a meeting was called “…to take such measures for Building a meeting house as a majority of Subscribers or proprietors may think proper.” After World War I, membership began to decline and from the 1930s until the society’s demise in 1957 services were infrequently held. In 1969 the property was acquired by the New Gloucester Historical Society, who maintained and restored the building. The flushboard siding, fully pedimented gable, pilasters, and symmetrical façade containing two entry doors, all work together to display the Greek Revival style in a high-style example, but in a rural setting. The building appears to be opened periodically by the Historical Society.