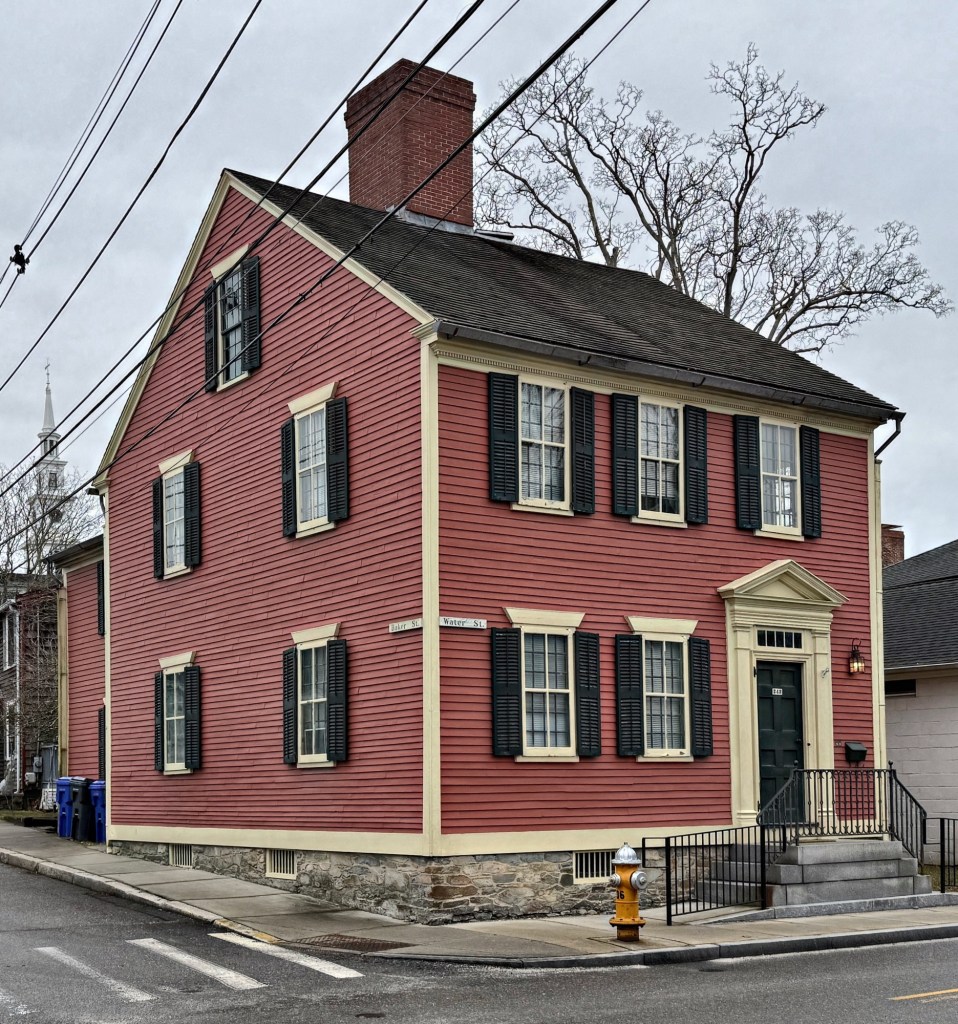
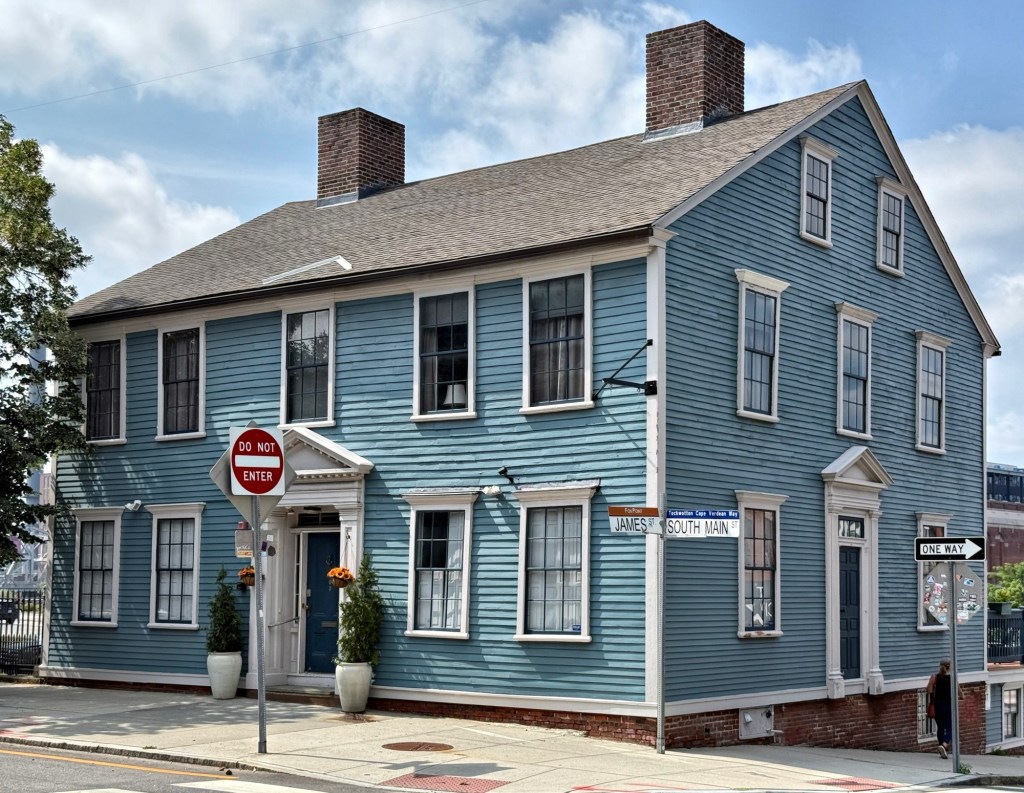
Located at the corner of Water and Baker streets in Warren, Rhode Island, this Georgian Colonial-era home oozes charm! Built by shipwright William Hill, as a three bay, two storied residence in 1761, this Colonial “half-house” was later owned by mariner William Collins who managed a wharf nearby. The home was later inherited by his son, Capt. Haile Collins (1798-1863). The two-story house with three-bay-façade and side-hall entry is a great example of a Georgian residence with raised stone foundation with entry accessed by double-run brownstone steps, massive central chimney, and the pedimented entry with transom and pilastered enframement. The home was eventually covered with asphalt shingle siding and was threatened with demolition in the 1980s until it was purchased and restored by Lombard John Pozzi, a prominent local force in architecture and historic preservation, who restored many old houses in the region.