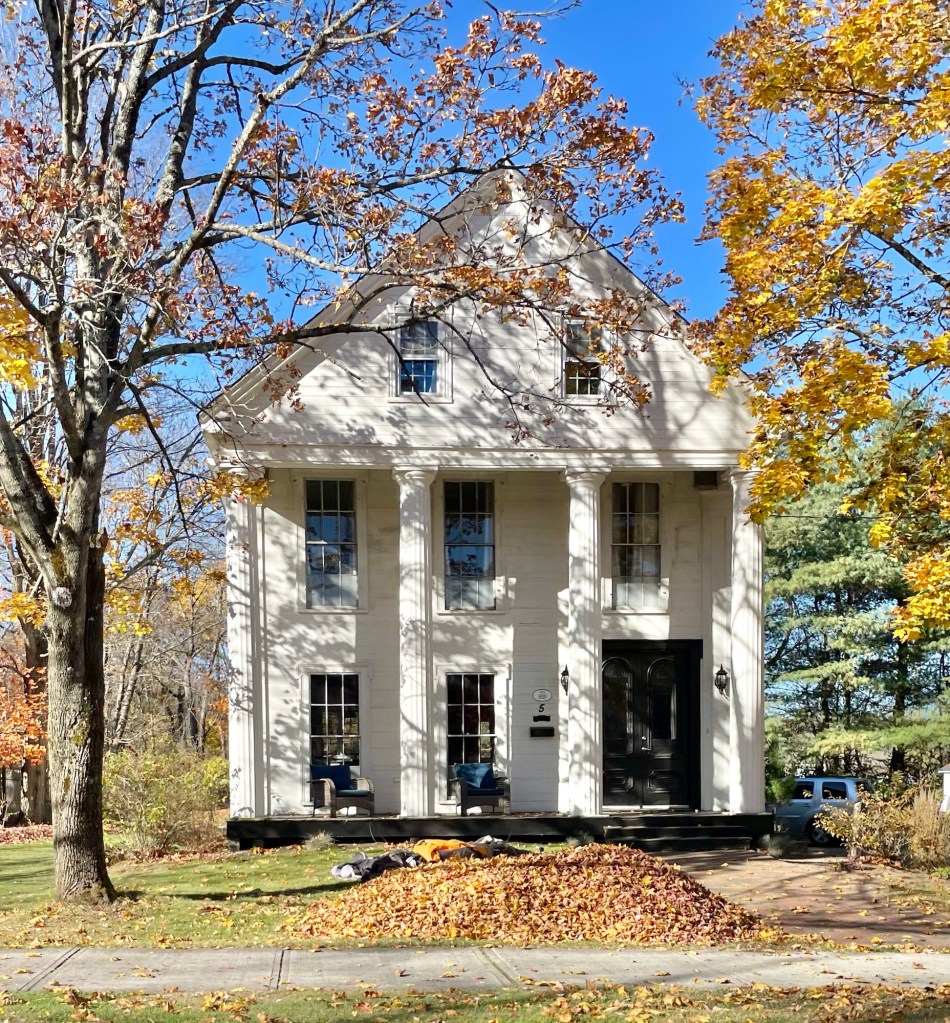
According to local histories, this significant Greek Revival style property on Elm Street in Georgetown, Massachusetts, was owned by Josiah Adams (1757-1852), a farmer, a Revolutionary War veteran, and a fourth-generation descendant of the immigrant Robert Adams, who arrived here from Devonshire, England by about 1629. In March 1849, the town’s Congregational Society purchased Adams Hall for eight hundred dollars to house the church vestry, which remained in the building for forty-one months until a new building was built for that purpose next door. Later, Adams Hall was owned by Moses Tenney (1808-1903), operator of a prosperous saw mill in Georgetown, and served at one time in the state senate. The structure retains its significant temple-front with four, two-story Doric columns supporting the portico. Also special on this residence is the use of flush-board siding and the oversized first floor windows.