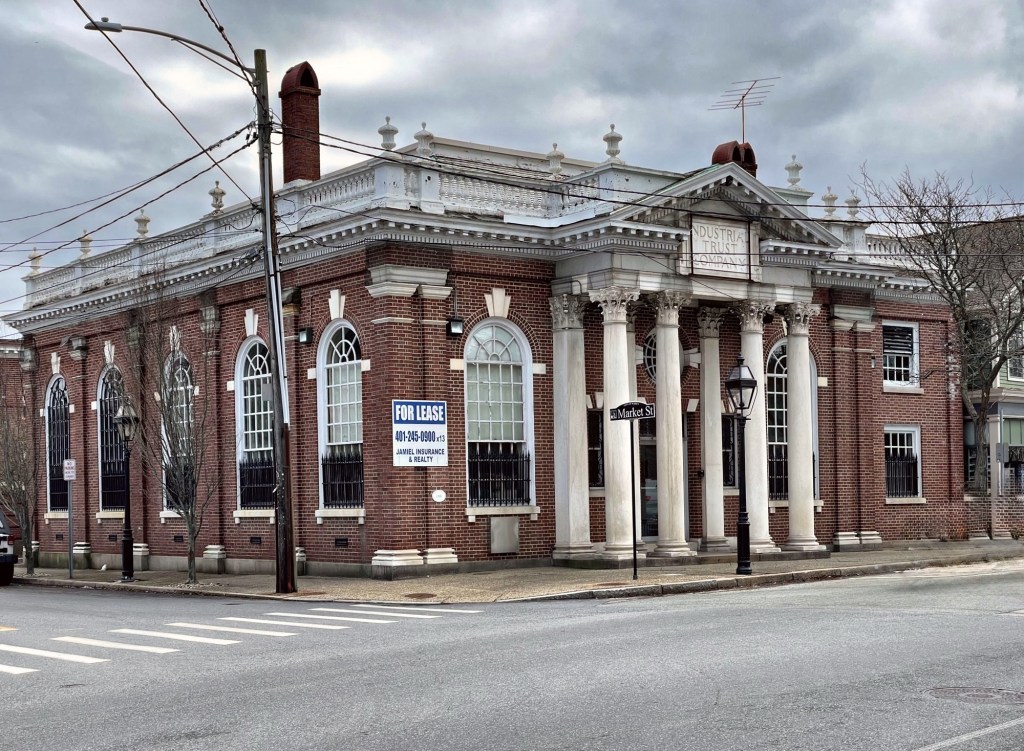
This monumental Georgian Revival bank building on Main Street in Warren, Rhode Island, and is one of the finest buildings of the style in the entire state. The Warren Industrial Trust in 1906 hired Edmund R. Willson of the Providence architectural firm of Stone, Carpenter & Willson to design the bank for the town after it had absorbed the town’s multiple banks, under one roof. It would be one of his final commissions before his death. On the facade, four Corinthian columns support a dentilled pediment over the entrance with the red brick walls enlivened with arched windows, oversized keystones, and pilasters with contrasting capitals and bases. The building shows that Colonial Revival architecture, while often seen as a refined, classical style, can be festive and ornate.